Creating an event trigger¶
Table of contents
Event triggers can be created using the Hasura console or metadata APIs.
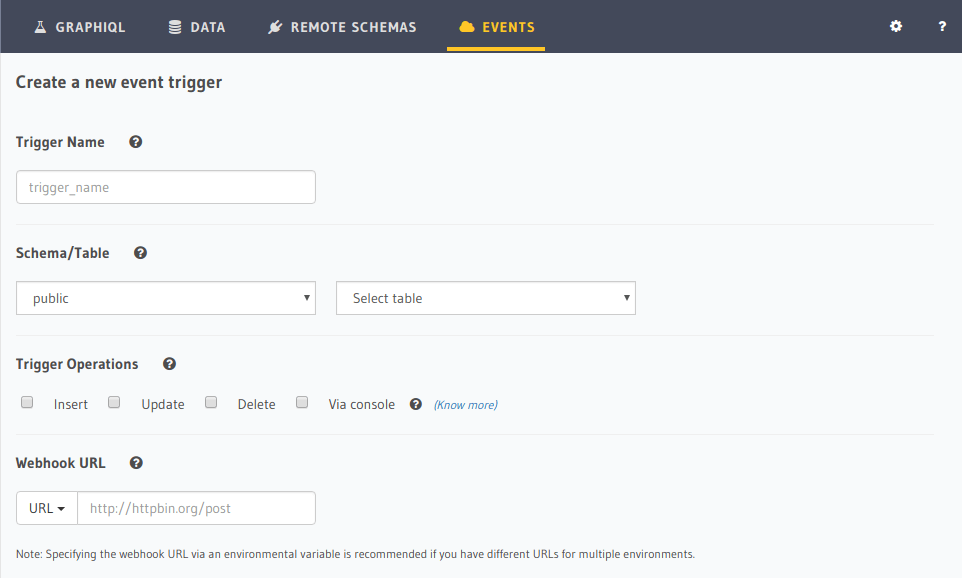
Open the Hasura console, head to the Events tab and click on the Create button to open the
page below:
Parameters¶
Trigger Name
Unique name for event trigger.
Schema/Table
The postgres schema and table name on which the event trigger needs to be created.
Trigger Operations
The table operation on which the event trigger will be invoked.
Webhook URL
The HTTP(s) URL which will be called with the event payload on configured operation. Must be a POST handler. This URL
can be entered manually or can be picked up from an environment variable (the environment variable needs to be set
before using it for this configuration).
Advanced Settings¶
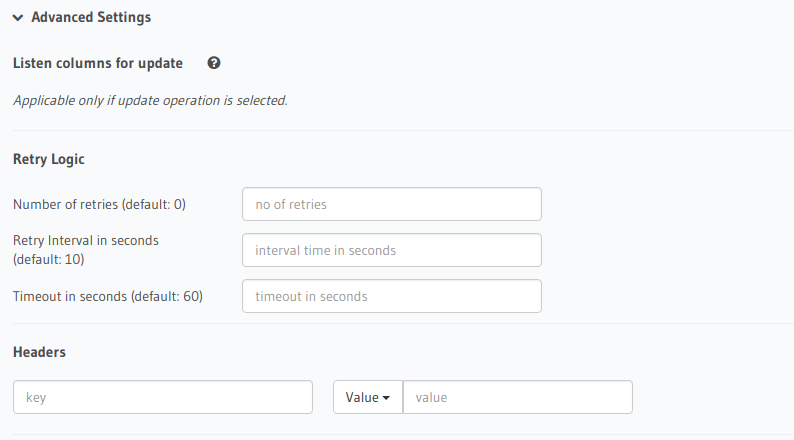
Listen columns for update¶
Update operations are special because you may want to trigger a webhook only if specific columns have changed in a row. Choose the columns here which you want the update operation to listen to.
If a column is not selected here, then an update to that column will not trigger the webhook.
Retry Logic¶
Retry configuration is available in the “Advanced settings” when you create a trigger.
num_retries: Number of times a failed invocation is retried. Default value is 0.interval_sec: Number of seconds after which a failed invocation is retried. Default value is 10.timeout_sec:: Number of seconds before which client closes the connection to the webhook. Default value is 60.
Headers¶
Custom headers can be added to an event trigger. Each webhook request will have these headers added.
Each header has 3 parameters:
Key: Name of the header e.g. Authorization or X-My-Header.Type: One ofstaticorfrom env variable.staticmeans the value provided in theValuefield is the raw value of the header.from env variablemeans the value provided in theValuefield is the name of the environment variable in the GraphQL engine which will be resolved before sending the header.Value: The value of the header. Either a static value or the name of an environment variable.
