Creating relationships¶
Table of contents
Introduction¶
A relationship from one table/view to another can be created by defining a link between a column of the table/view to a column of the other table/view.
Typically, relationships are defined using foreign-key constraints. But in some cases, it might not be possible to use foreign-key constraints to create the relation. For example, while trying to create a relationship involving a view as foreign-keys can’t be created on views.
Using foreign keys¶
Say we created two tables, author(id, name) and article(id, title, content, rating, author_id).
Let us now connect these tables to enable nested queries using a foreign-key:
Step 1: Add foreign-key constraint¶
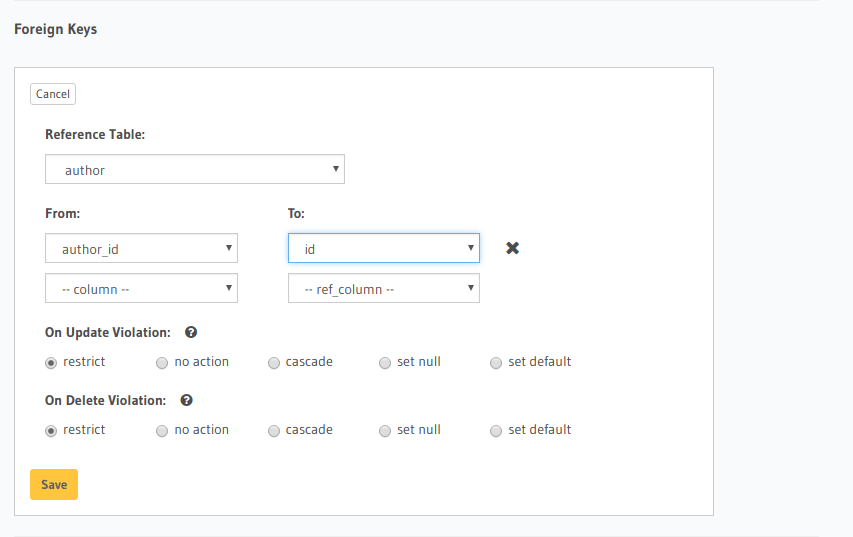
In the console, navigate to the Modify tab of the article table. Click the Add button in
the Foreign Keys section and configure the author_id column as a foreign-key for the id column in
the author table:
Step 2: Create an object relationship¶
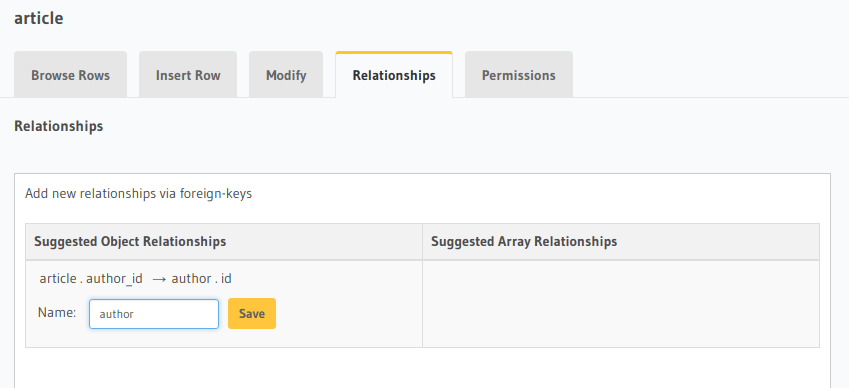
Each article has one author. This is an object relationship.
The console infers this using the foreign-key created above and recommends the potential relationship in the
Relationships tab of the article table.
Add an object relationship named author for the article table as shown here:
We can now run a nested object query that is based on this object relationship.
Fetch a list of articles and each article’s author:
query {
article {
id
title
author {
id
name
}
}
}
Step 3: Create an array relationship¶
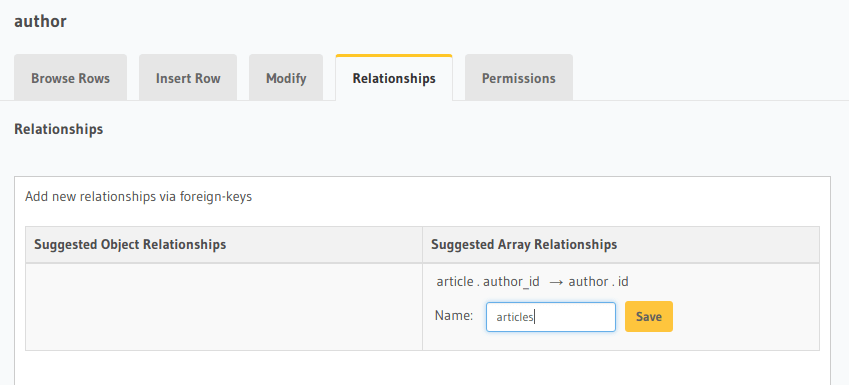
An author can write multiple articles. This is an array relationship.
You can add an array relationship in the same fashion as an object relationship as shown above.
Add an array relationship named articles for the author table as shown here:
We can now run a nested object query that is based on this array relationship.
Fetch a list of authors and a nested list of each author’s articles:
query {
author {
id
name
articles {
id
title
}
}
}
Using manual relationships¶
Let’s say you have a table author (id, name) and a view author_avg_rating (id, avg) which has the
average rating of articles for each author.
Let us now create an object relationship called avg_rating from the author table to the
author_avg_rating view using a manual relationship:
Step 1: Open the manual relationship section¶
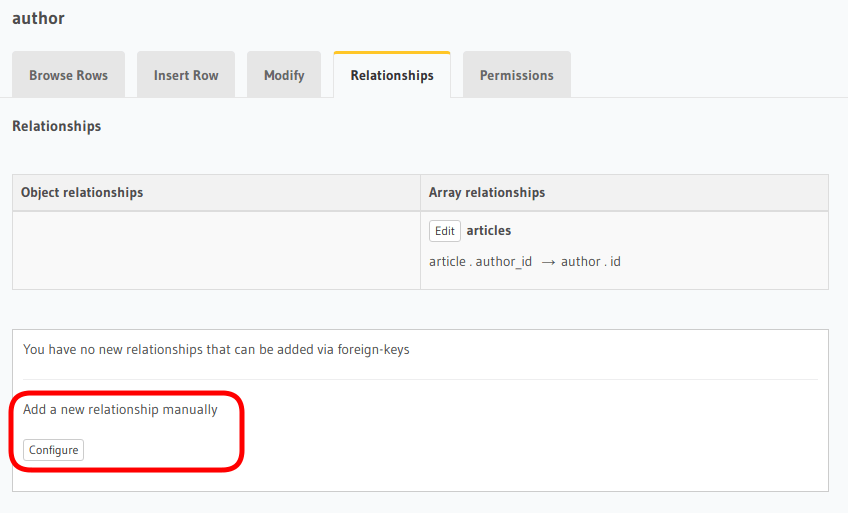
- Open the console and navigate to the
Data -> author -> Relationshipstab. - Click on the
Configurebutton:
Step 2: Define the relationship¶
The above step will open up a section as shown below:
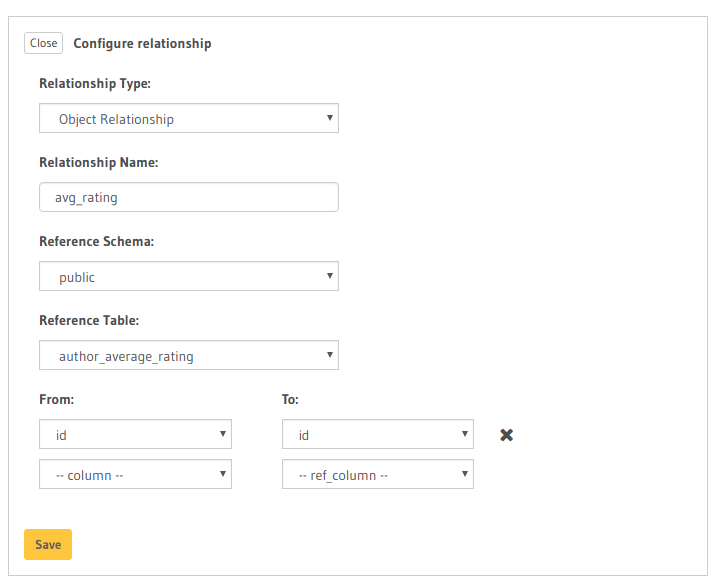
In this case:
- Relationship Type will be:
Object Relationship - Relationship Name can be:
avg_rating - Reference will be:
id -> author_avg_rating . id(similar to defining a foreign-key)
Step 3: Create the relationship¶
Now click on the Save button to create the relationship.
We can now run a nested object query that is based on this object relationship.
Fetch a list of authors with the average rating of their articles:
query {
author {
id
name
avg_rating {
avg
}
}
}
